Introduction
Stoppage time in soccer is the extra time a referee adds at the end of each half to make up for lost play. It covers delays caused by injuries, substitutions, fouls, and goal celebrations.
Understanding stoppage time matters because it often decides match outcomes, from World Cup finals to local derbies. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what stoppage time is, how it’s calculated, why it’s used, and answer the most common questions fans ask.
What Is Stoppage Time in Soccer?
Stoppage time is the additional time added to the end of each 45-minute half to compensate for interruptions during play.
Unlike American football or basketball, the soccer clock never stops. Instead, referees keep track of delays like injuries or time-wasting and add minutes back after the 45th or 90th minute. For example, a half with multiple substitutions and an injury might see 3–5 minutes of stoppage time.
This ensures fairness: every game still delivers a full 90 minutes of active play.
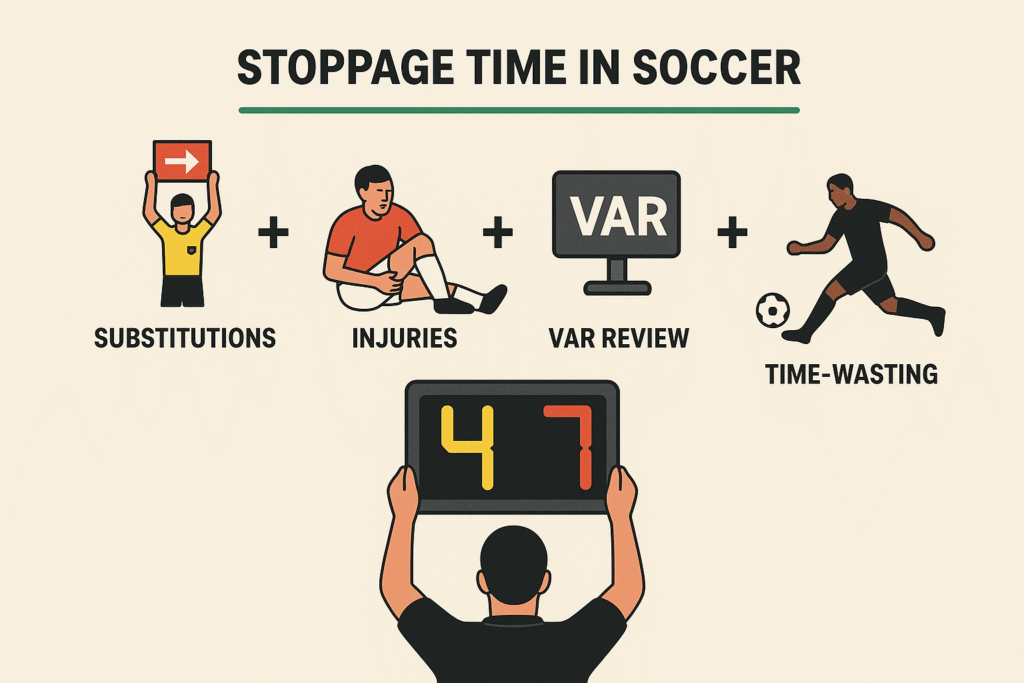
How Is Stoppage Time Calculated in Soccer?
The referee calculates stoppage time based on lost minutes during the half. The fourth official then displays the minimum time on a board near the 45th and 90th minutes.
Factors influencing stoppage time include:
- Substitutions: Around 30 seconds per change.
- Injuries: Minor injuries may add 1–2 minutes, while serious ones can extend it by 5 minutes or more.
- VAR (Video Assistant Referee) checks: Reviews for goals, penalties, or red cards extend play.
- Goal celebrations: Typically 30–60 seconds each.
- Time-wasting tactics: Slow throw-ins, delayed free kicks, or goalkeeper stalling.
- External delays: Equipment issues, pitch invasions, or weather.
👉 Key detail: The number displayed is always the minimum. The referee can extend play further if more stoppages occur during stoppage time itself.
Common Questions About Stoppage Time
Why doesn’t soccer stop the clock like other sports?
Soccer prioritizes continuous flow. Stopping the clock would break rhythm, so referees manage lost time silently and add it at the end.
Who decides stoppage time in soccer?
The referee on the field. The fourth official only announces it; the referee has the final authority.
Can stoppage time be shorter than shown?
No. The time displayed is the minimum. The referee can let play continue longer but never end it earlier.
Is stoppage time the same in all leagues?
Yes, the principle is universal under FIFA’s Laws of the Game. However, strictness may vary. For instance, the 2022 FIFA World Cup featured unusually long stoppage times to better reflect delays.
What is the difference between stoppage time and extra time?
- Stoppage time = minutes added at the end of a half.
- Extra time = two 15-minute halves played only in knockout games when scores are tied.
Additional FAQs
Why is stoppage time sometimes called injury time?
Historically, injuries were the biggest cause of delays, so fans started calling it “injury time.” Today, it covers all interruptions, not just injuries.
What is the longest stoppage time in soccer history?
In some matches, especially during the 2022 World Cup, stoppage times exceeded 14 minutes. In lower leagues, extreme cases of 20+ minutes have occurred.
Can goals be scored in stoppage time?
Yes. Matches often feature dramatic stoppage-time winners or equalizers, famously nicknamed “Fergie Time” during Sir Alex Ferguson’s Manchester United era.
Why was stoppage time so long in the Qatar 2022 World Cup?
FIFA instructed referees to be stricter in accounting for delays, especially VAR checks and goal celebrations, leading to 8–12 minutes of added time in many games.
Practical Tips for Watching Stoppage Time
- Check the board: The fourth official announces the minimum added minutes at the 45th and 90th minute.
- Expect surprises: A game showing 4 minutes may last 5 or more if there are late fouls or substitutions.
- Never tune out early: Some of the most famous goals in soccer history—like Sergio Agüero’s Premier League title winner in 2012—came in stoppage time.
Comparisons with Other Sports
Soccer’s stoppage time system is unique. In sports like basketball or hockey, the clock pauses during interruptions, making time visible to fans. Soccer instead relies on referee discretion, creating unpredictability.
This unpredictability fuels excitement, but it also sparks debate. Some critics argue for a transparent, stopped clock. However, FIFA maintains that stoppage time preserves soccer’s flow and drama.
Conclusion
Stoppage time in soccer is the referee’s method of restoring fairness by adding minutes lost to injuries, substitutions, celebrations, and time-wasting. While it may appear subjective, it ensures every match delivers a full 90 minutes of play.
Far from being just “extra minutes,” stoppage time is often when history is written—last-gasp goals, title deciders, and unforgettable drama. So next time the board goes up, remember: in soccer, it’s not over until the referee blows the final whistle.
